# Gin
# 1. HelloWorld
package main
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
r.GET("/ping", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.JSON(200, gin.H{
"message": "pong",
})
})
r.Run()
}
# 2. gin.New vs gin.Default
gin.Default 有 Logger 和 Recovery。
# 3. 路由
# 3.1 基本路由
- router.GET
- router.POST
- router.DELETE
- router.PUT
# 3.2 路由分组
- group1 := router.Group("group1")
- group1.GET
- group1.POST
- group1.DELETE
- group1.PUT
# 4. 参数
# 4.1 url 中的变量
package main
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
g1 := r.Group("goods")
// 使用冒号 : 获取 url 中参数 id 的值
// 使用 * 号来获取 /* 后面的所有路径,在“文件路径”场景使用
g1.GET("/:id/*action", getGoodsByIdAndAction)
r.Run()
}
func getGoodsByIdAndAction(c *gin.Context) {
id := c.Param("id")
action := c.Param("action")
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"id": id,
"action": action,
})
}
访问:http://localhost:8080/goods/22/222/hello/11
输出:
{"action":"/222/hello/11","id":"22"}
# 4.2 参数约束
可以通过 c.ShouldBindUri(&object) 来限制 url 中参数的数据类型
package main
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
// 限制参数类型
type Person struct {
// required 表示必须带上
ID string `uri:"id" binding:"required"`
Name string `uri:"name" binding:"required"`
}
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
r.GET("/:name/:id", func(c *gin.Context) {
var person Person
// 参数类型必须满足 Person 结构体中的属性类型
if err := c.ShouldBindUri(&person); err != nil {
c.Status(404)
return
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"name": person.Name,
"id": person.ID,
})
})
r.Run()
}
# 4.3 GET 中的 Query
- c.Query("paramName")
- c.DefaultQuery("paramName", "defaultValue")
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
r.GET("/hello", func(c *gin.Context) {
id := c.Query("id")
name := c.Query("name")
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"name": name,
"id": id,
})
})
r.Run()
}
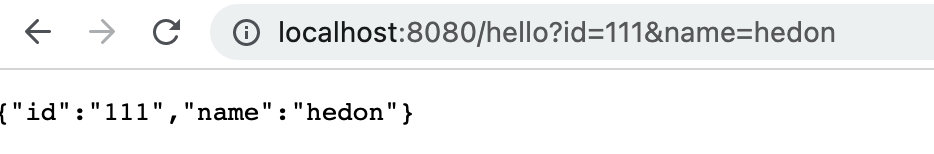
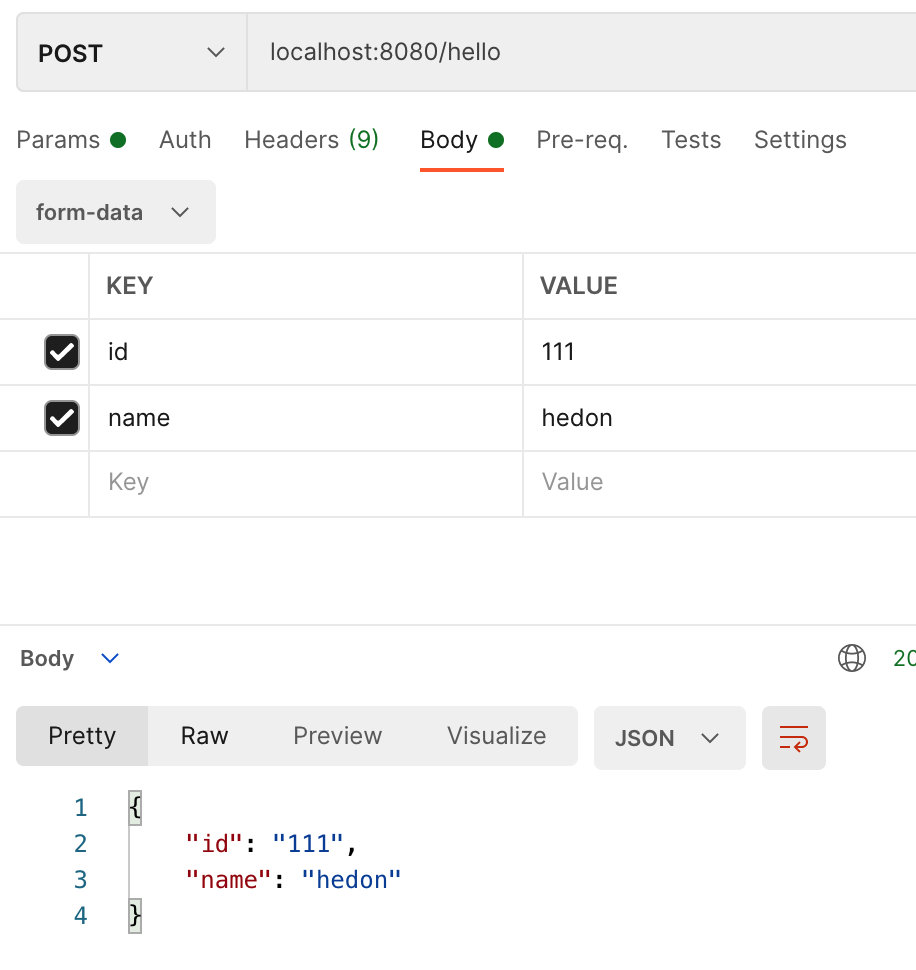
# 4.4 POST 中的 form-data
- c.PostForm("paramName")
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
r.POST("/hello", func(c *gin.Context) {
id := c.PostForm("id")
name := c.PostForm("name")
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"name": name,
"id": id,
})
})
r.Run()
}
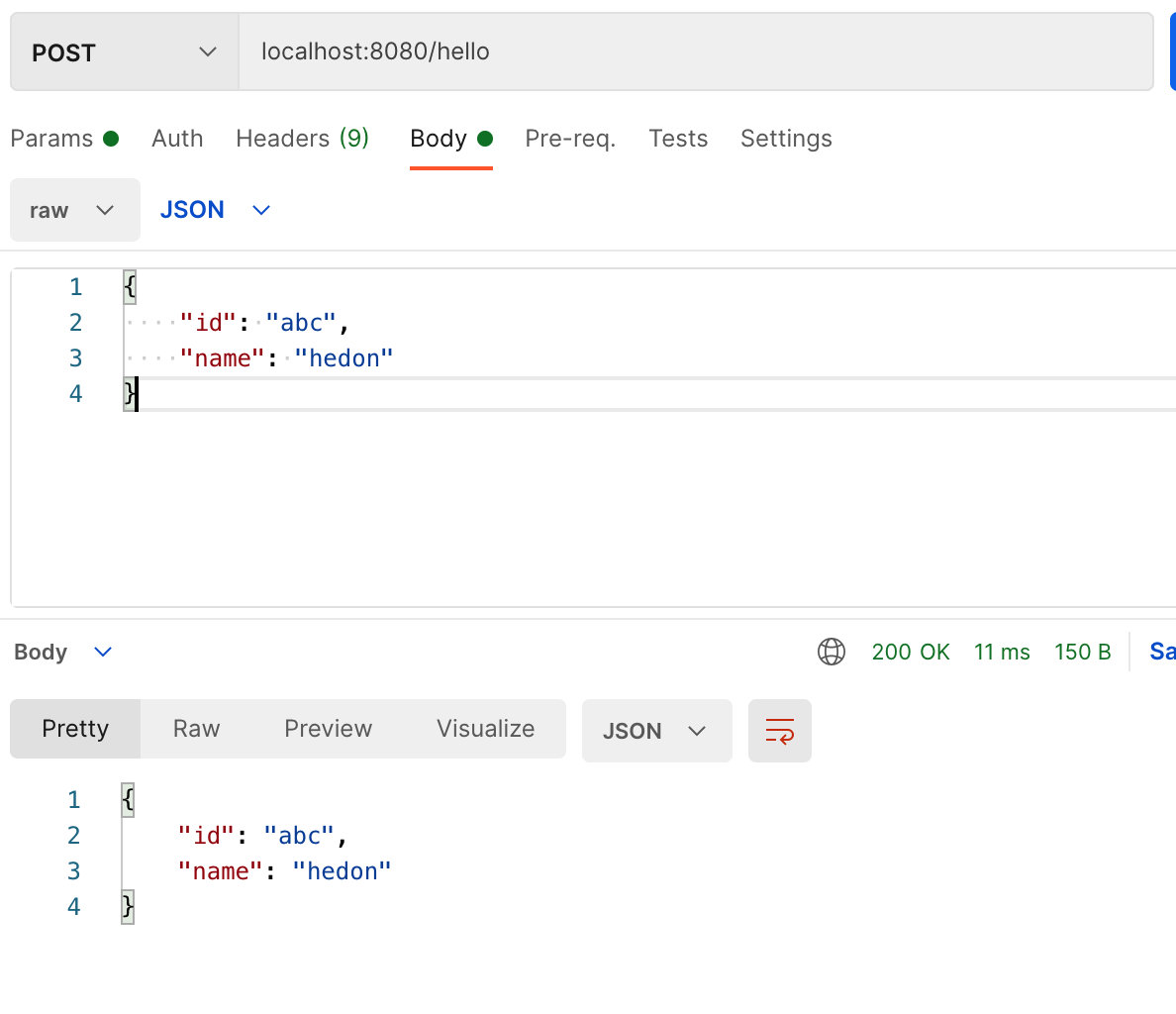
# 4.5 POST 中的 body
type Param struct {
Name string `json: "name"`
Id string `json: "id"`
}
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
r.POST("/hello", func(c *gin.Context) {
// 获取 requestBody
body := c.Request.Body
// 读取 requestBody
paramBytes, err := ioutil.ReadAll(body)
if err != nil {
c.Status(404)
return
}
var param Param
// 序列化 body
err = json.Unmarshal(paramBytes, ¶m)
if err != nil {
c.Status(500)
return
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"name": param.Name,
"id": param.Id,
})
})
r.Run()
}
# 5. 输出
# 5.1 输出 JSON
ginContext.JSON(statusCode, gin.H{ ... })
ginContext.JSON.JSON(statusCode, structInstance)
ginContext.PureJSON(statusCode, gin.H{ ... })
通常情况下,JSON 会将特殊的 HTML 字符串替换为对应的 unicode 字符,比如
<替换为\u003c,如果想输出原样的 HTML,则使用 PureJSON。
# 5.2 输出 ProtoBuf
- ginContext.ProtoBuf(statusCode, protoObject)
# 6. 表单验证
# 6.1 基本验证
若要在请求主体绑定到结构体中,请使用模型绑定,目前支持 JSON、XML、YAML 和标准表单(foo=bar&boo=baz)的绑定。
Gin 使用 go-playground/validator 验证参数。
需要在绑定的字段上设置 tag,比如,绑定格式为 JSON,需要这样设置 json:"fieldName"。此外,Gin 还提供了两套绑定方法:
- Must bind
- Methods -
Bind、BindJson、BindXML、BindQuery、BindYAML - Behavior - 这些方法底层使用
MustBindWith,如果存在绑定错误,请求将会被以下指令终止c.AbortWithError(400, err).SetTtype(ErrorTypeBind),响应状态码会被设置为 400,请求头Content-Type会被设置为text/plain;charset=utf-8。注意,如果你试图在此之后设置响应码,则会发出一个警告[Gin-debug][Warning] Headers were already written. Wanted to override status code 400 with 422,如果你希望更好地控制行为,请使用ShouldBind相关方法。
- Methods -
- Should bind
- Methods -
ShouldBind、ShoudBindJSON、ShoudBindXML、ShouldBindQuery - Behavior - 这些方法底层使用
ShouldBindWith,如果存在绑定错误,则返回错误,开发人员可以正确处理请求和错误。
- Methods -
当我们使用绑定方法时,Gin 会根据 Context-Type 推断出使用哪种绑定器。
还可以给字段指定特定规则的修饰符,如果一个字段用 binding: "required" 修饰,并且在绑定时该字段的值为空,那么将返回一个错误。
# 6.2 错误信息中文化
validator 库中提供了错误信息的翻译案例,具体可看:translations-example (opens new window)。
# 7. 中间件
- router.User(middleware ...gin.HandlerFunc)
