# JavaSE —— BIO/NIO/AIO
# 一、网络编程基础
# 1. URL 的解析和构造

URI 和 URL 的区别与联系
- URI: Uniform Resource Identifier
- URL: Uniform Resource Locator
- URN: Uniform Resource Name
URI 是抽象的定义,不管用什么方法表示,只要能定位一个资源,就叫 URI,本来设想的的使用两种方法定位:
- URL:用地址定位
- URN:用名称定位
# 2. DNS 解析
域名 -> IP 地址
# 3. 网络协议
# 4. Java IO
- 参考:JavaSE —— IO
# 5. Socket
对于底层网络应用开发者而言,几乎所有网络编程都是 Socket,因为大部分底层网络 的编程都离不开 Socket 编程。 HTTP 编程、 Web 开发、 IM 通信 、视频流传输的底层都是 Socket 编程 。
日常生活中我们每天打开浏览器浏览网页、使用 QQ 聊天、 邮件收发、 直播等,客户端和服务器端的通信在底层看来都是依靠 Socket 通信的。
Socket 起源于 UNIX,而 UNIX 的基本哲学之一就是“一切皆文件”,都可以用 “打开(open)→读写(write/read)→关闭(close)” 模式来操作, Socket 就是该模式的一个实现,网络的 Socket 数据传输是 一种特殊的 I/0,Socket 也是一种文件描述符。 Socket 也具有一个类似于打开文件的函数调用:Socket(), 该函数返回一个整型的 Socket 描述符, 随后的连接建立、数据传输等操作都是通过该 Socket 实现的 。
网络中的进程之间如何通过 Socket 通信呢?首要解决的问题是如何唯一标识一个进程,否则通信无从谈起 ! 在本地可以通过进程 PID 来唯一标识一个进程,但是在网络中这是行不通的。其实 TCP/IP 协议族己经帮我们解决了这个问题,网络层的“IP 地址”可以唯一标识网络中的主机,而传输层的“协议+端口” 可以唯一标识主机中的应用程序(进程)。这样利用三大要素(IP 地址、协议、端口)就可以标识网络的进程了,网络中需要互相通信的进程,就可以利用这个标志在它们之间进行交互。
使用 TCP/IP 协议的应用程序通常采用应用编程接口:UNIX BSD 的套接字和 UNIX System V 的 TLI(己经被淘汰),来实现网络进程之间的通信。就目前而言, 几乎所有的应用程序都是采用 Socket,而现在又是网络时代,网络中进程通信是无处不在的,这就是为什么说“一切皆 Socket”。
Socket 有两种:
- TCPSocket
- UDP Socket
TCP 和 UDP 是协议,而要确定一个进程得需要三要素, 所以还需要 IP 地址和端口。
# 6. 阻塞/非阻塞 vs 异步/同步
阻塞/非阻塞
👀 从调用方的角度来看)
- 如果调用方在被调用方返回结果之前只能傻傻等待,那就是阻塞的。
- 如果调用方在被调用方返回结果之前可以先干别的事情,那就是非阻塞的。
同步/异步
(从被调用方的角度来看👀
- 如果被调用方被调用之后需要立刻返回结果,那么就是同步的。
- 如果被调用方被调用之后先返回一个空的结果,等到任务执行完成后再通知调用方,那就是异步的。
同步和异步的区别:是否开启新线程。
阻塞和非阻塞的区别:当前线程是否挂起,即是否释放 CPU。
# 7. Linux 5 种 IO
- 参考:Linux IO
# 二、BIO
# 1. 简介
- Java BIO 就是传统的 java io 编程,其相关接口在 java.io。
- BIO(Blocking I/O):同步阻塞,服务器实现模式为一个连接一个线程,即客户端有连接请求时,服务器端就需要一个启动一个线程进行处理,如果这个连接不做任何事情会造成不必要的线程开销,可以通过线程池机制改善(实现多个客户连接服务器)。
- BIO 适用于连接数目较小且固定架构,这种方式对服务器资源要求较高,并发局限于应用中,JDK1.4 之前的唯一选择,程序简单易理解。
# 阻塞体现在哪里?
accept() :阻塞接收客户端的连接
read()/write()
connect():和服务端建立连接,连接的过程中 connect() 会阻塞
# 2. 编程模型
- 服务器启动一个 ServerSocket;
- 客户端启动 Socket 对服务器进行通信,默认情况下服务器需要对每个客户建立一个线程与之通讯;
- 客户端发出请求后,先咨询服务器,是否有线程响应,如果没有则会等待,或者被拒绝;
- 如果有响应,客户端线程会等待请求结束后,再继续执行。
# 3. 缺点
- 每个请求都需要创建独立线程,与对应的客户端进行数据 Read 业务处理,数据 Write。
- 当并发数量较大,需要创建大量线程来处理连接,系统资源占用较大。
- 连接建立后,如果当前线程没有数据可读,则线程就阻塞在 Read 操作上,造成线程资源浪费。
# 4. 实战多人聊天室
# 4.1 架构设计
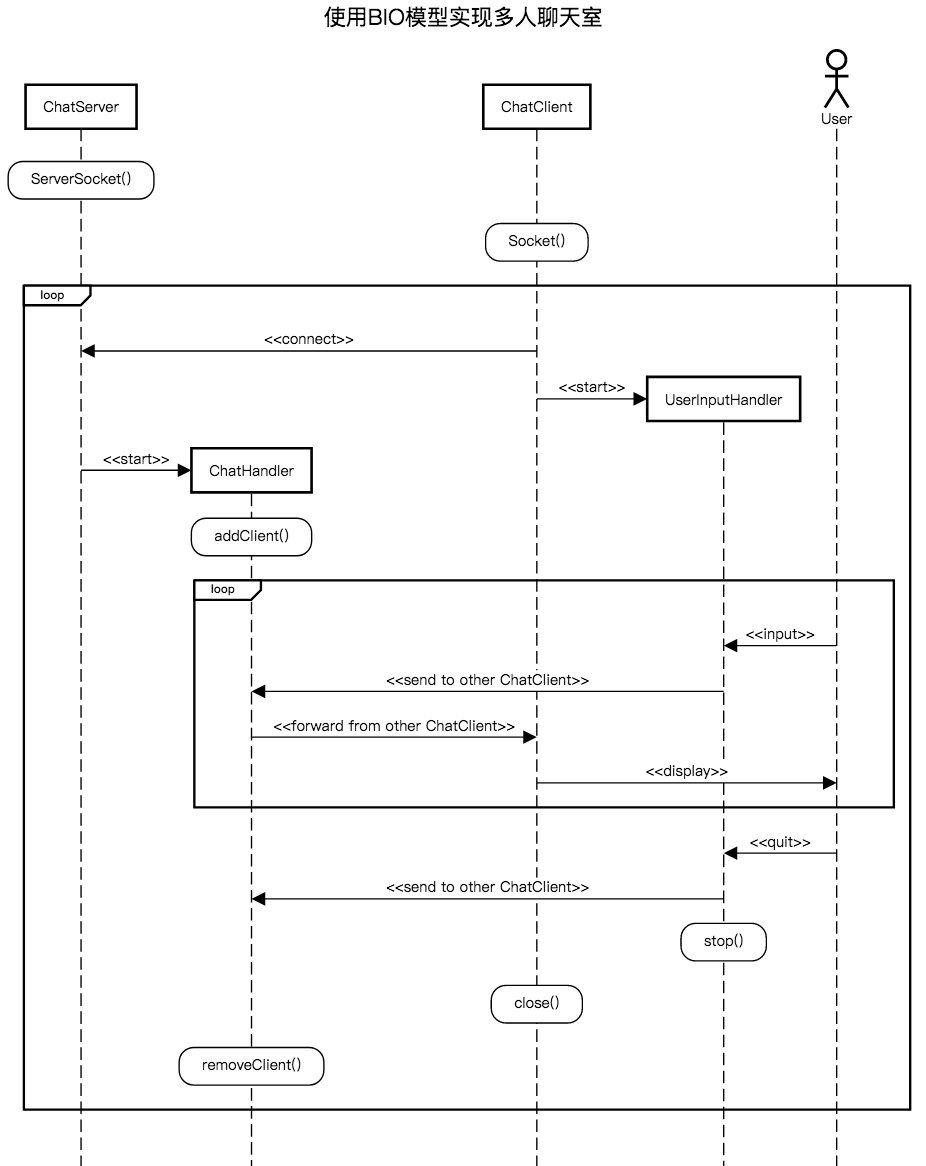
服务端:
- 一个线程来负责添加和删除客户端,并维护一个在线的客户端列表;
- 一个线程来负责接收和广播客户端的信息;
客户端:
- 一个线程来负责等待用户输入;
- 一个线程来负责接收其他客户端发来的信息;
# 目录结构
.
├── client
│ ├── ChatClient.java
│ ├── ChatClientStarter.java
│ └── UserInputHandler.java
└── server
├── ChatHandler.java
├── ChatServer.java
└── ChatServerStarter.java
# 4.2 服务端实现
ChatServer
public class ChatServer { private int DEFAULT_PORT = 8888; // 默认端口 private final String QUIT = "quit"; // 客户端退出命令 private ServerSocket serverSocket; // socket private ExecutorService executorService; // 线程池 private HashMap<Integer, Writer> connectedClients; // 端口:写对象 public ChatServer() { connectedClients = new HashMap<>(); executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10); } /** * 客户端上线 * @param socket accept 到的客户端 socket * @throws IOException 获取 socket 的 outputStream 时可能抛出 IOException */ public synchronized void addClient(Socket socket) throws IOException{ if (socket != null) { int port = socket.getPort(); BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter( new OutputStreamWriter(socket.getOutputStream()) ); // 添加 connectedClients.put(port, writer); // 日志 System.out.println("客户端 [" + port + "] 已连接到服务器"); } } /** * 客户端下线 * @param socket accept 到的客户端 socket * @throws IOException 关闭 socket 的 outputStream 时可能抛出 IOException */ public synchronized void removeClient(Socket socket) throws IOException { if (socket != null){ int port = socket.getPort(); if (connectedClients.containsKey(port)) { // 关闭 writer 对象 connectedClients.get(port).close(); // 移除 connectedClients.remove(port); // 日志 System.out.println("客户端 [" + socket.getPort() + "] 已下线"); } } } /** * 服务端转发信息给除发送者之外的所有客户端 * @param socket 发送者 * @param message 消息 * @throws IOException 向 socket 的 outputStream 进行写操作时可能抛出 IOException */ public synchronized void forwardMessage(Socket socket, String message) throws IOException { if (socket != null && !message.isEmpty()) { for (Integer port: connectedClients.keySet()) { if (!port.equals(socket.getPort())) { Writer writer = connectedClients.get(port); writer.write(message); writer.flush(); } } } } /** * 检查用户是否准备退出 */ public boolean readyToQuit(String msg) { return QUIT.equals(msg); } /** * 服务端主线程 * 1. 监听客户端,等待客户端连接 * 2. 接收客户端信息,并进行转发 * 3. 维护在线的客户端列表 */ public void start(){ try { // 绑定监听端口 serverSocket = new ServerSocket(DEFAULT_PORT); System.out.println("启动服务器,监听端口:" + DEFAULT_PORT + "..."); // 监听客户端请求 Socket accept; while (true) { // 等待客户端连接 accept = serverSocket.accept(); // 创建 ChatHandler 线程 executorService.execute(new ChatHandler(this, accept)); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { close(); } } /** * 关闭服务器 */ private synchronized void close(){ if (serverSocket != null){ try { serverSocket.close(); System.out.println("服务器正常退出..."); }catch (IOException e) { System.out.println("服务器退出异常..."); e.printStackTrace(); } } } }ChatHandler
public class ChatHandler implements Runnable{ private ChatServer chatServer; // 服务端 private Socket socket; // 客户端 public ChatHandler(ChatServer chatServer, Socket socket) { this.chatServer = chatServer; this.socket = socket; } @Override public void run() { try { // 存储新上线的客户端 chatServer.addClient(socket); System.out.println("添加客户端 [" + socket.getPort() + "] 成功!"); // 读取用户发送的信息 BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader( new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()) ); String msg = null; while ((msg = reader.readLine()) != null) { // 检查用户是否是退出命令 if (chatServer.readyToQuit(msg.trim())) { break; } // 转发消息到其他在线的客户端 chatServer.forwardMessage(socket, "客户端 [" + socket.getPort() + "]: " + msg + "\n"); } } catch (IOException e) { System.out.println("添加客户端 [" + socket.getPort() + "] 失败..."); e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { // 移除客户端 chatServer.removeClient(socket); } catch (IOException e) { System.out.println("客户端 [" + socket.getPort() + "] 下线异常..."); e.printStackTrace(); } } } }ChatServerStarter
public class ChatServerStarter { public static void main(String[] args) { ChatServer chatServer = new ChatServer(); chatServer.start(); } }
# 4.3 客户端实现
ChatClient
public class ChatClient { private final String DEFAULT_SERVER_HOST = "127.0.0.1"; // 服务端主机 private final int DEFAULT_SERVER_PORT = 8888; // 服务端端口 private final String QUIT = "quit"; // 客户端退出命令 private Socket socket; // 客户端 socket private BufferedReader reader; private BufferedWriter writer; /** * 发送消息 */ public void sendMessage(String message) throws IOException { if (socket != null && !socket.isOutputShutdown()) { if (writer != null) { writer.write(message + "\n"); writer.flush(); } } } /** * 接收消息 */ public String receiveMessage() throws IOException { if (socket != null && !socket.isInputShutdown()) { if (reader != null) { return reader.readLine(); } } return null; } /** * 检查用户是否准备退出 */ public boolean readyToQuit(String message) { return QUIT.equals(message); } /** * 启动客户端 */ public void start() { try { // 创建 socket,绑定服务端 socket = new Socket(DEFAULT_SERVER_HOST, DEFAULT_SERVER_PORT); // 创建 IO 流 reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream())); writer = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(socket.getOutputStream())); // 处理用户输入 new Thread(new UserInputHandler(this)).start(); // 读取服务器转发的其他客户端的信息 String message = null; while ((message = receiveMessage()) != null) { System.out.println(message); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { close(); } } /** * 关闭客户端 */ private void close() { if (reader != null) { try { reader.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (writer != null) { try { writer.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (socket != null) { try { socket.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }UserInputHandler
public class UserInputHandler implements Runnable{ private ChatClient chatClient; // 对应的客户端 public UserInputHandler(ChatClient chatClient) { this.chatClient = chatClient; } @Override public void run() { // 等待用户输入消息 BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); String message = null; try { while (true) { // 读取用户输入 message = reader.readLine(); // 向服务器发送消息 chatClient.sendMessage(message); // 检查用户是否准备退出 if (chatClient.readyToQuit(message)) { break; } } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { reader.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }ChatClientStarter
public class ChatClientStarter { public static void main(String[] args) { ChatClient chatClient = new ChatClient(); chatClient.start(); } }
# 4.4 演示

# 三、NIO
# 1. BIO 中的阻塞
- ServerSocket.accept()
- InputStream.read()
- OutputStream.writer()
- 无法在同一个线程里面处理多个 Stream I/O
# 2. 简介
NIO 中的 N 可以理解为 Non-blocking,不单纯是 New。它支持面向缓冲的,基于通道的 I/O 操作方法。 NIO 提供了与传统 BIO 模型中的 Socket 和 ServerSocket 相对应的 SocketChannel 和 ServerSocketChannel 两种不同的套接字通道实现。两种通道都支持阻塞和非阻塞两种模式。
阻塞模式使用就像传统中的支持一样,比较简单,但是性能和可靠性都不好;非阻塞模式正好与之相反。
对于低负载、低并发的应用程序,可以使用同步阻塞 I/O 来提升开发速率和更好的维护性;对于高负载、高并发的(网络)应用,应使用 NIO 的非阻塞模式来开发。
# 3. 特点
- 使用 Channel 代替 Stream
- 使用 Selector 监控多条 Channel
- 可以在一个线程里处理多个 Channel I/O
# 4. Buffer

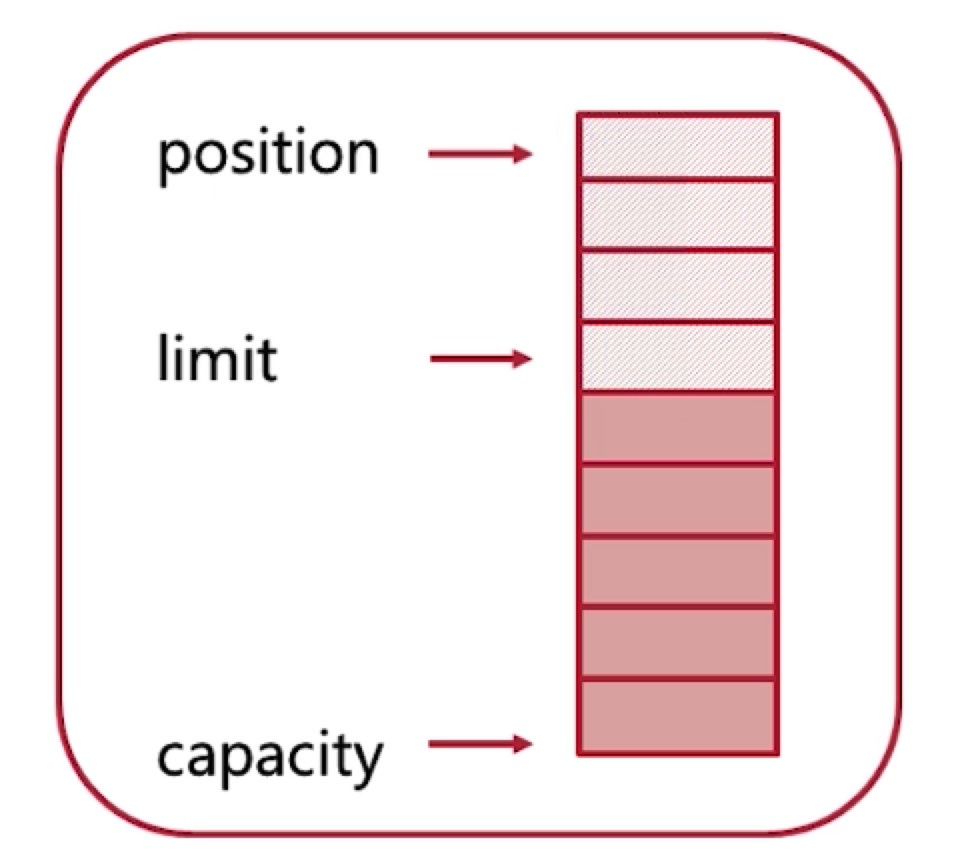
- position: 当前指针
- limit: 能写或者能读的最远地方
- capacity: 缓冲区容量
# 4.1 向 Buffer 写入数据
- 从 position 位置写,然后移动 position 指针,在到达 limit 之前都是可以写的
# 4.2 从 Buffer 读取数据
- 调用
flip()方法,将 Buffer 的写模式反转成读模式; flip()放把 position 移动回写的初始位置,然后把 limit 移动到刚刚写入的最远位置;
# 4.2 刷新 Buffer
- Buffer 里所有数据都已经被读完了,调用
clear():- 会把 position 和 limit 都复原到原位置。
- Buffer 里面数据只读了一半,调用
clear():- 会调用
compact()方法把未读的位置挪到前面,然后移动 position 指针到已有数据的下面,然后继续接受写或者读。
- 会调用
# 5. Channel
Channel 通过 Buffer 来写入和读取数据,Channel 也可以直接跟 Channel 进行数据的传输。
几个重要的 Channel:
- FileChannel
- SocketChannel
- ServerSocketChannel
# 6. 多种方式实现本地文件拷贝
interface FileCopyRunner {
void copyFile(File source, File target);
}
public class FileCopyDemo {
// 性能测试
private static void benchmark(FileCopyRunner fileCopyRunner) {
Date start = new Date();
File source = new File("a.txt");
File target = new File("b.txt");
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
fileCopyRunner.copyFile(source, target);
}
Date end = new Date();
System.out.println("总时间:" + (end.getTime() - start.getTime()));
}
// 关闭资源
private static void closeResource(Closeable closeable) {
if (closeable != null){
try {
closeable.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* ① BIO: 不利用缓冲区
*/
FileCopyRunner noBufferStreamCopy = new FileCopyRunner() {
@Override
public void copyFile(File source, File target) {
InputStream fin = null;
OutputStream fout = null;
try {
fin = new FileInputStream(source);
fout = new FileOutputStream(target);
// 读文件
int result;
while ( (result = fin.read() ) != -1) {
// 写文件
fout.write(result);
}
} catch (IOException e ) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
closeResource(fin);
closeResource(fout);
}
}
};
/**
* ② BIO: 利用缓冲区
*/
FileCopyRunner bufferredStreamCopy = new FileCopyRunner() {
@Override
public void copyFile(File source, File target) {
InputStream fin = null;
OutputStream fout = null;
try {
fin = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(source));
fout = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(target));
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int result;
// 读
while ((result = fin.read(buffer)) != -1) {
// 写
fout.write(buffer, 0, result);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
closeResource(fin);
closeResource(fout);
}
}
};
/**
* ③ NIO: 利用缓冲区
*/
FileCopyRunner nioBufferCopy = new FileCopyRunner() {
@Override
public void copyFile(File source, File target) {
FileChannel fin = null;
FileChannel fout = null;
try {
// 通过文件流来获取对应通道
fin = new FileInputStream(source).getChannel();
fout = new FileOutputStream(target).getChannel();
// 缓冲区
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
// 读数据,写 Buffer
while ( fin.read(byteBuffer) != -1) {
// 需要将 Buffer 从写模式转移到读模式
byteBuffer.flip();
// 读 Buffer,传进 channel
while (byteBuffer.hasRemaining()) {
fout.write(byteBuffer);
}
// 读模式再转为写模式
byteBuffer.compact();
byteBuffer.clear();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
closeResource(fin);
closeResource(fout);
}
}
};
/**
* ④ NIO: 不利用缓冲区,channel 直接交互
*/
FileCopyRunner nioTransferCopy = new FileCopyRunner() {
@Override
public void copyFile(File source, File target) {
FileChannel fin = null;
FileChannel fout = null;
try {
fin = new FileInputStream(source).getChannel();
fout = new FileOutputStream(target).getChannel();
// channel 直接传输
long hasTransferred = 0L;
while (hasTransferred != fin.size()) {
hasTransferred += fin.transferTo(hasTransferred, fin.size(), fout);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
closeResource(fin);
closeResource(fout);
}
}
};
// 测试
System.out.print("noBufferStreamCopy ");
benchmark(noBufferStreamCopy);
System.out.print("bufferredStreamCopy ");
benchmark(bufferredStreamCopy);
System.out.print("nioBufferCopy ");
benchmark(nioBufferCopy);
System.out.print("nioTransferCopy ");
benchmark(nioTransferCopy);
}
}
输出:
noBufferStreamCopy 总时间:25588
bufferredStreamCopy 总时间:206
nioBufferCopy 总时间:271
nioTransferCopy 总时间:240
经过多次实验,得出结论:
- 文件大的话,使用 Channel 的优势会更明显;
- Buffer 的用处非常大;
- 单线程下 BIO 和 NIO 区别不大,多线程下 NIO 的优势明显;
# 7. Selector
Selector 是用来管理 Channel 的一个工具,开发者可以将 Channel 注册到特定的 Selector,Selector 会为 Channel 生成一个 SelectorKey,然后就可以通过 SelectorKey 的各种方法来管理 Channel,如以下方法:
- interestOps(): 开发者希望 Selector 监控到 Channel 的哪些状态;
- readyOps(): 获得目前的 Channel 处于哪些可操作的状态;
- channel(): 返回对应的 Channel 对象;
- selector(): 返回 Channel 所注册 Selector 对象;
- attachment(): 开发者可以将任意对象附着在 Channel 上,通过该方法可以获取该对象;
其中 Ops 代表了 Channel 的某种状态,也可以理解为 Channel 所监听的某种事件,有如下:
- CONNECT
- ACCEPT
- READ
- WRITE
Selector 对象有以下方法可以获取 Channel 的信息:
- select(): 返回有几个 Channel 处于满足 Selector 所监听的状态;
# 8. 编程模型

# 9. 实战多人聊天室
# 9.1 架构设计
与 BIO 不同的是,NIO 的实现方式不需要再手动维护一个 Map,因为 Selector 会维护一个所有注册到它上面 SelectionKey 组成的 Set。
另外,NIO 也不需要每连接一个客户端就派一个线程去处理,而是支持在单线程下对多个客户端进行处理,因为用到了 Channel,而 Selector 又可以用来管理 Channel。
读写数据都是要经过 Buffer 的,且要注意,每次往 Buffer 里面写完东西后,都需要调用 flip() 将 Buffer 从写模式切换到读模式:
- 写数据:先写到 wBuffer,再转到 Channel
- 读数据:从 Channel 将数据读到 rBuffer,再冲 rBuffer 中读出数据
# 目录结构
├── client
│ ├── ChatClient.java
│ ├── ChatClientStarter.java
│ └── UserInputHandler.java
└── server
├── ChatServer.java
└── ChatServerStarter.java
# 9.2 服务端实现
ChatServer
public class ChatServer { private static final int DEFAULT_PORT = 8888; private static final String QUIT = "quit"; private static final int BUFFER = 1024; private ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel; private Selector selector; private ByteBuffer rBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(BUFFER); private ByteBuffer wBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(BUFFER); private Charset charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8"); private int port; public ChatServer(){ this(DEFAULT_PORT); } public ChatServer(int port){ this.port = port; } /** * 启动服务端 */ public void start(){ try { // 获得服务端的通道 serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); // 修改为非阻塞模式 serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false); // 绑定端口 serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(this.port)); // 获得 Channel 控制器 Selector 对象 selector = Selector.open(); // 将服务端 Channel 注册到 Selector 中,注册 ACCEPT 事件 serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); System.out.println("启动服务器,监听端口:" + this.port + "..."); // Selector 监听事件 while (true) { selector.select(); // 处理所有被触发的事件 Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys(); for (SelectionKey selectionKey : selectionKeys){ handles(selectionKey); } // 清空之前的事件集 selectionKeys.clear(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { closeResource(selector); } } /** * 处理被触发的事件 */ private void handles(SelectionKey selectionKey) throws IOException { // ACCEPT 事件 —— 即和客户端建立连接 if (selectionKey.isAcceptable()) { ServerSocketChannel server = (ServerSocketChannel)selectionKey.channel(); // 获取客户端 channel SocketChannel client = server.accept(); // 将客户端 channel 转为非阻塞模式 client.configureBlocking(false); // 为客户端 channel 注册 READ 事件 // 当 READ 事件触发时,表示有客户端写东西了,channel 有可以读的东西 client.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); System.out.println(getClientName(client) + "已连接"); } // READ 事件 —— 即客户端发来信息,需要转发给其他客户端 else if (selectionKey.isReadable()) { SocketChannel client = (SocketChannel)selectionKey.channel(); // 获取客户端发来的信息 String fwdMsg = receive(client); if (fwdMsg.isEmpty()) { // 空信息 -> 客户端异常 -> 退出客户端 selectionKey.cancel(); selector.wakeup(); } else { System.out.println(getClientName(client) + ": " + fwdMsg); // 转发信息 forwardMessage(client, fwdMsg); // 判断用户是否准备退出 if (readyToQuit(fwdMsg)){ selectionKey.cancel(); selector.wakeup(); System.out.println(getClientName(client) + "已断开"); } } } } /** * 将 client 发来的信息转发给其他客户端 */ private void forwardMessage(SocketChannel client, String fwdMsg) throws IOException { for (SelectionKey key : selector.keys()) { Channel connectedChannel = key.channel(); // 不转发给服务端 if (connectedChannel instanceof ServerSocketChannel) { continue; } // 不转发给自身 if (key.isValid() && connectedChannel instanceof SocketChannel && !client.equals(connectedChannel)) { wBuffer.clear(); // 先将数据写到 wBuffer 中 wBuffer.put(charset.encode(getClientName(client) + ": " + fwdMsg)); wBuffer.flip(); // 将从 rBuffer 将数据送到 channel while (wBuffer.hasRemaining()){ ((SocketChannel)connectedChannel).write(wBuffer); } } } } /** * 接收客户端发来的信息 */ private String receive(SocketChannel client) throws IOException { rBuffer.clear(); // 将 channel 数据读到 rBuffer while (client.read(rBuffer) > 0) {} // 将 rBuffer 的写模式转为读模式 rBuffer.flip(); return String.valueOf(charset.decode(rBuffer)); } /** * 构建客户端名称 */ private String getClientName(SocketChannel client) { return "客户端 [" + client.socket().getPort() + "] "; } /** * 判断客户端是否准备退出 */ private boolean readyToQuit(String msg) { return QUIT.equals(msg); } /** * 释放资源 */ private void closeResource(Closeable closable) { if (closable != null) { try { closable.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }ChatServerStarter
public class ChatServerStarter { public static void main(String[] args) { ChatServer chatServer = new ChatServer(7777); chatServer.start(); } }
# 9.3 客户端实现
ChatClient
public class ChatClient { private static final String DEFAULT_SERVER_HOST = "127.0.0.1"; private static final int DEFAULT_SERVER_PORT = 8888; private static final String QUIT = "quit"; private static final int BUFFER = 1024; private String host; private int port; private SocketChannel clientSocketChannel; private ByteBuffer rBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(BUFFER); private ByteBuffer wBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(BUFFER); private Selector selector; private Charset charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8"); public ChatClient() { this(DEFAULT_SERVER_HOST, DEFAULT_SERVER_PORT); } public ChatClient(String host, int port) { this.host = host; this.port = port; } /** * 启动客户端 */ public void start(){ try { // 获取客户端 channel clientSocketChannel = SocketChannel.open(); // 设置为非阻塞模式 clientSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false); // 创建一个通道管理器 selector selector = Selector.open(); // channel 注册 CONNECT 事件到 selector clientSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT); // 连接服务端 clientSocketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(this.host, this.port)); // 监听事件 while (true){ selector.select(); Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys(); for (SelectionKey key : selectionKeys) { handles(key); } selectionKeys.clear(); } }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ClosedSelectorException e) { // 正常退出,无需处理 } finally { closeResource(selector); } } /** * 处理被触发的事件 */ private void handles(SelectionKey key) throws IOException { // CONNECT 事件 —— 客户端已经连接上服务端了 if (key.isConnectable()) { SocketChannel client = (SocketChannel)key.channel(); // 判断是否已经完成连接 if (client.isConnectionPending()) { client.finishConnect(); // 处理用户输入 new Thread(new UserInputHandler(this)).start(); } // 注册 READ 事件 client.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); } // READ 事件 —— 服务端转发别的客户端的消息过来 else if (key.isReadable()) { SocketChannel clientSocketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel(); String msg = receive(clientSocketChannel); if (msg.isEmpty()) { // 空信息 -> 服务端异常 -> 客户端退出 closeResource(selector); } else { System.out.println(msg); } } } /** * 从通道中读取信息 */ private String receive(SocketChannel clientSocketChannel) throws IOException { rBuffer.clear(); while (clientSocketChannel.read(rBuffer) > 0){} rBuffer.flip(); return String.valueOf(charset.decode(rBuffer)); } /** * 发送消息 */ public void send(String input) throws IOException { if (input.isEmpty()) { return; } // 先写入 wBuffer wBuffer.clear(); wBuffer.put(charset.encode(input)); wBuffer.flip(); // 再转到 channel while (wBuffer.hasRemaining()){ clientSocketChannel.write(wBuffer); } // 监控用户是否退出 if (readyToQuit(input)) { closeResource(selector); } } /** * 判断客户端是否准备退出 */ public boolean readyToQuit(String msg) { return QUIT.equals(msg); } /** * 释放资源 */ private void closeResource(Closeable closable) { if (closable != null) { try { closable.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }UserInputHandler
public class UserInputHandler implements Runnable { private ChatClient chatClient; public UserInputHandler(ChatClient chatClient){ this.chatClient = chatClient; } @Override public void run() { try { // 等待用户输入消息 BufferedReader consoleReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); while (true) { String input = consoleReader.readLine(); // 像服务器发送消息 chatClient.send(input); // 检查用户是否退出 if (chatClient.readyToQuit(input)) { break; } } }catch (IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } }ChatClientStarter
public class ChatClientStarter { public static void main(String[] args) { ChatClient chatClient = new ChatClient("127.0.0.1", 7777); chatClient.start(); } }
# 9.4 演示

# 四、AIO
# 1. 简介
与 NIO 不同,使用 AIO 进行读写操作时,只须直接调用 API 的 read 或 write 方法即可。这两种方法均为异步的:
- 对于读操作而言,当有流可读取时,操作系统会将可读的流传入
read方法的缓冲区,并通知应用程序; - 对于写操作而言,当操作系统将
write方法传递的流写入完毕时,操作系统主动通知应用程序。
即可以理解为,read/write 方法都是异步的,完成后会主动调用回调函数。 在 JDK1.7 中,这部分内容被称作 NIO.2,主要在java.nio.channels 包下增加了下面四个异步通道:
- AsynchronousSocketChannel
- AsynchronousServerSocketChannel
- AsynchronousFileChannel
- AsynchronousDatagramChannel
其中的 read/write 方法,会返回一个带回调函数的对象,当执行完读取/写入操作后,直接调用回调函数。
# 2. 异步实现
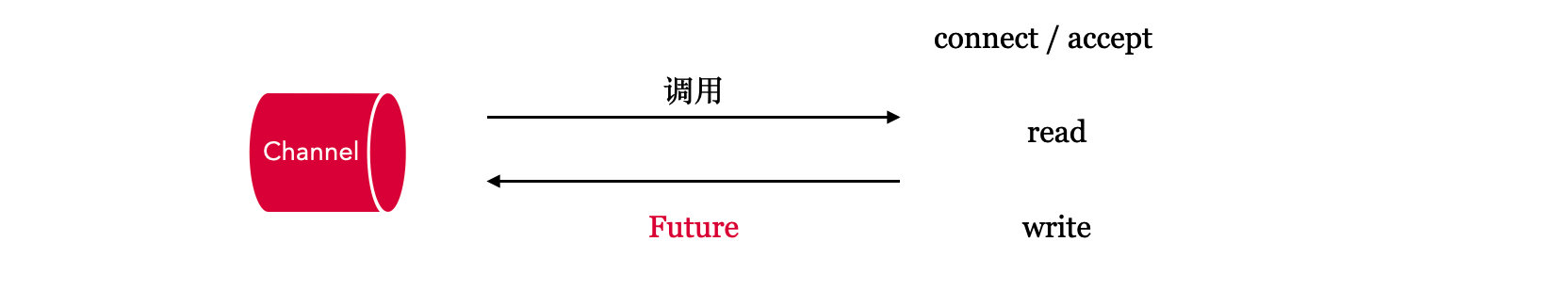
# 2.1 通过 Future
# 2.2 通过 CompletionHandler

# 3. 原理
# 4. 编程模型
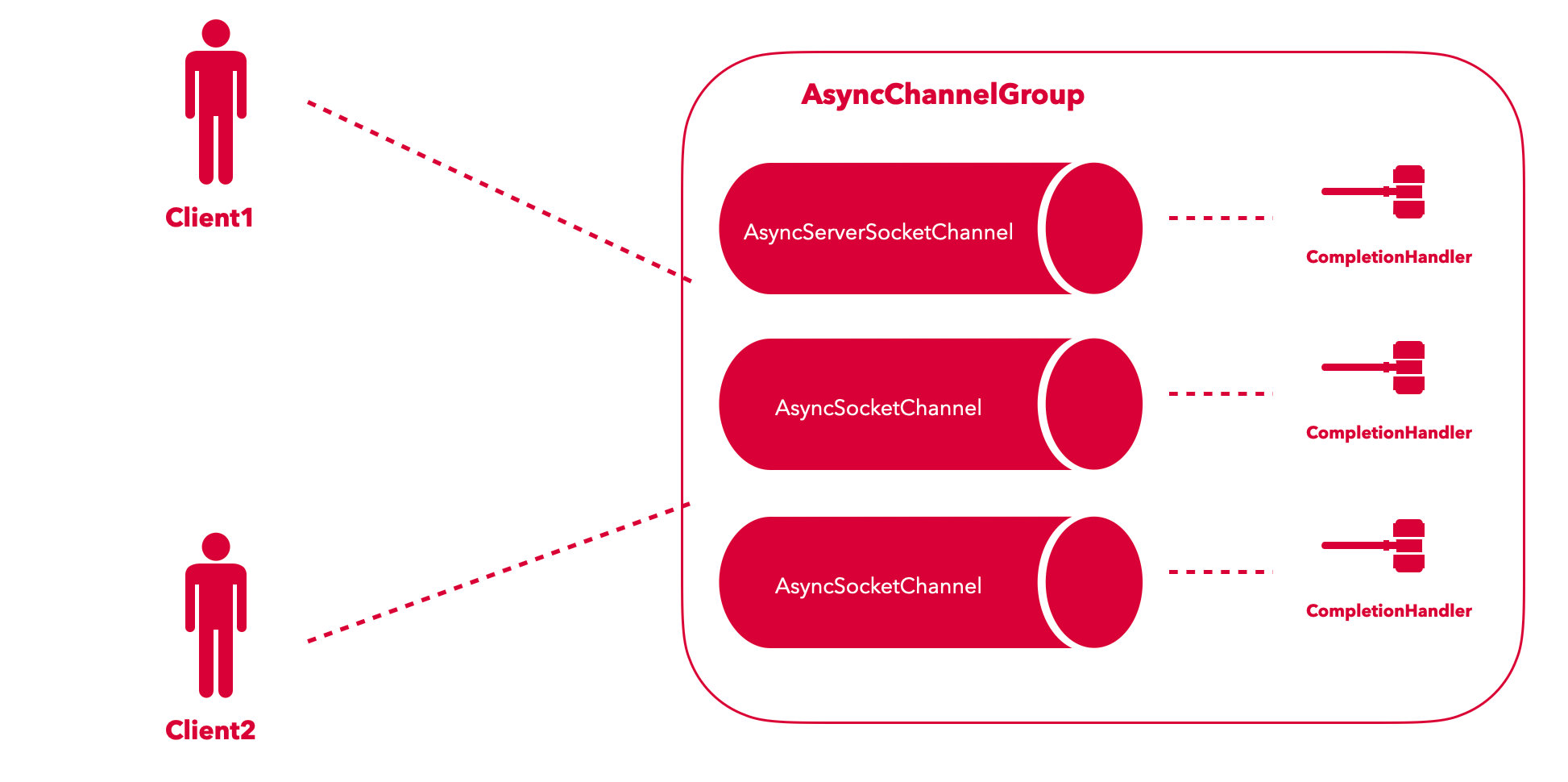
# 5. 实现“回音壁”
- 服务器端采用 CompletionHandler 来实现异步
- 客户端采用 Future 来实现异步
Server:
public class Server {
final String LOCALHOST = "localhost";
final int DEFAULT_PORT = 8888;
final int BUFFER = 1024;
final String READ_OP = "read";
final String WRITE_OP = "write";
AsynchronousServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Server server = new Server();
server.start();
}
/**
* 启动服务端
*/
public void start(){
try {
// 绑定监听端口
serverSocketChannel = AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(LOCALHOST, DEFAULT_PORT));
System.out.println("启动服务器,监听端口:" + DEFAULT_PORT + "...");
// 监听客户端,accept 的第二个参数就是一个回调函数 CompletionHandler
while (true) {
// 异步,直接返回
serverSocketChannel.accept(null, new AcceptHandler());
// 阻塞一下,避免一直循环
System.in.read();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
closeResource(serverSocketChannel);
}
}
/**
* 释放资源
*/
private void closeResource(Closeable closeable) {
if(closeable != null){
try{
closeable.close();
System.out.println("关闭" + closeable);
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* IO 完成后要调用的回调
*
* CompletionHandler<V,A>
* @param '<V>' The result type of the I/O operation 这里我们要返回的就是客户端对应的异步通道
* @param '<A>' The type of the object attached to the I/O operation 要附带的对象的类型
*/
private class AcceptHandler implements CompletionHandler<AsynchronousSocketChannel, Object>{
/**
* IO 正常结束后要做的事情
*/
@Override
public void completed(AsynchronousSocketChannel result, Object attachment) {
// 服务端还在线的话,要继续监听
if (serverSocketChannel.isOpen()){
serverSocketChannel.accept(null, this);
}
// 处理客户端请求
AsynchronousSocketChannel clientChannel = result;
if (clientChannel != null && clientChannel.isOpen()) {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(BUFFER);
// attachment
Map<String, Object> info = new HashMap<>();
info.put("type", READ_OP);
info.put("buffer", buffer);
// 参数1:目标 Buffer
// 参数2:attachment
// 参数3:IO 完成后要执行的回调
clientChannel.read(buffer, info, new ClientHandler(clientChannel));
}
}
/**
* IO 异常后要做的事情
*/
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, Object attachment) {
System.out.println("AcceptHandler 出现异常了,exception: " + exc.toString() + ",attachment:" + attachment.toString());
}
}
/**
* 读取完客户端发来的信息后要执行的回调
*
* CompletionHandler<Integer,? super A> handler
* @param '<Integer>' The result type of the I/O operation 这里是返回读到了多少个字节
* @param '<? super A>' The type of the object attached to the I/O operation 需要是 A 的父类,A 是 attachment
*/
private class ClientHandler implements CompletionHandler<Integer, Map<String, Object>>{
private AsynchronousSocketChannel clientChannel;
public ClientHandler(AsynchronousSocketChannel clientChannel) {
this.clientChannel = clientChannel;
}
/**
* IO 正常结束后要做的事情
*/
@Override
public void completed(Integer result, Map<String, Object> attachment) {
String type = (String) attachment.get("type");
// READ -> 即服务端收到来自客户端的信息了
if (type.equals(READ_OP)) {
// 回音壁:读出客户端发来的数据,然后再回传回去
ByteBuffer buffer = (ByteBuffer) attachment.get("buffer");
// 从写模式切换为读模式
buffer.flip();
// 将 buffer 中的数据写进 channel 中
attachment.put("type", WRITE_OP);
clientChannel.write(buffer, attachment, this);
buffer.clear();
}
// WRITE -> 即服务端回传数据了
else if (type.equals(WRITE_OP)){
// 服务端回传完后让服务端继续监听客户端有可能发来的数据
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(BUFFER);
attachment.put("type", READ_OP);
attachment.put("buffer", buffer);
clientChannel.read(buffer, attachment, this);
}
}
/**
* IO 异常后要做的事情
*/
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, Map<String, Object> attachment) {
System.out.println("ClientHandler 出现异常了,exception: " + exc.toString() + ",attachment:" + attachment.toString());
}
}
}
Client:
public class Client {
final String LOCALHOST = "localhost";
final int DEFAULT_PORT = 8888;
AsynchronousSocketChannel clientSocketChannel;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Client client = new Client();
client.start();
}
/**
* 启动客户端
*/
public void start(){
try {
// 连接服务端
clientSocketChannel = AsynchronousSocketChannel.open();
// 获得 Future 对象
Future<Void> connectFuture = clientSocketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(LOCALHOST, DEFAULT_PORT));
// ========================================
// 此处可以加一些其他的操作,因为可以是异步非阻塞的
// ========================================
// 等待连接建立完成
connectFuture.get();
// 处理用户输入
while (true) {
BufferedReader consoleReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String input = consoleReader.readLine();
byte[] inputBytes = input.getBytes();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(inputBytes);
// 传给服务端
Future<Integer> writeFuture = clientSocketChannel.write(buffer);
// ========================================
// 此处可以加一些其他的操作,因为可以是异步非阻塞的
// ========================================
// 等待写入完成
writeFuture.get();
// 读取服务器返回的消息
buffer.flip();
buffer.clear();
Future<Integer> readFuture = clientSocketChannel.read(buffer);
// ========================================
// 此处可以加一些其他的操作,因为可以是异步非阻塞的
// ========================================
// 等待读取完成
readFuture.get();
String echo = new String(buffer.array());
buffer.clear();
System.out.println("服务端:" + echo);
}
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
closeResource(clientSocketChannel);
}
}
/**
* 释放资源
*/
private void closeResource(Closeable closeable) {
if(closeable != null){
try{
closeable.close();
System.out.println("关闭" + closeable);
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
演示:

# 6. 实战多人聊天室
# 6.1 架构设计
跟 BIO 很像,只不过这会儿是异步的。在服务端我们采用 CompletionHandler 来实现异步,在客户端我们采用 Future 来实现异步。
# 目录结构
├── client
│ ├── ChatClient.java # 客户端实现
│ ├── ChatClientStarter.java # 客户端启动器
│ └── UserInputHandler.java # 处理用户输入
└── server
├── AcceptHandler.java # 客户端连接到服务器时的回调
├── ChatServer.java # 服务端实现
├── ChatServerStarter.java # 服务端启动器
└── ClientHandler.java # 服务器收到客户端信息时的回调
# 6.2 服务端实现
ChatServer
public class ChatServer { private static final String LOCALHOST = "localhost"; private static final int DEFAULT_PORT = 8888; private static final int THREAD_POOL_SIZE = 8; private AsynchronousChannelGroup channelGroup; // 自定义 asyncChannelGroup private AsynchronousServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel; // 服务端异步通道 private List<ClientHandler> connectedClients; private int port; public ChatServer(){ this(DEFAULT_PORT); } public ChatServer(int port){ this.port = port; this.connectedClients = new ArrayList<>(); } /** * 启动服务器 */ public void start() { // 定义一个线程池,给 channel group 用 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(THREAD_POOL_SIZE); try { // 自定义 asyncChannelGroup channelGroup = AsynchronousChannelGroup.withThreadPool(executorService); // 开一个服务端通道 serverSocketChannel = AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open(channelGroup); // 绑定端口 serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(LOCALHOST, this.port)); System.out.println("启动服务端,监听端口:" + this.port + "..."); // 监听客户端的连接请求 while (true) { // 参数1:附带对象 // 参数2:客户端连接后要进行的回调 serverSocketChannel.accept(null, new AcceptHandler(this.serverSocketChannel, this.connectedClients)); // 阻塞一下,避免一直循环。 // accept 后,read 前可以做其他一些操作,因为是异步非阻塞的 System.in.read(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { closeResource(serverSocketChannel); if (channelGroup != null) { channelGroup.shutdown(); } } } /** * 释放资源 */ private void closeResource(Closeable closeable){ if (closeable != null){ try { closeable.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }ChatServerStarter
public class ChatServerStarter { public static void main(String[] args) { new ChatServer(9999).start(); } }AcceptHandler
/** * 客户端连接完成后要做的回调 * * @param '<V>' The result type of the I/O operation 这里要返回的是客户端对应的异步通道 * @param '<A>' The type of the object attached to the I/O operation 附加对象的类型 */ public class AcceptHandler implements CompletionHandler<AsynchronousSocketChannel, Object> { private static final int BUFFER = 1024; private AsynchronousServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel; private List<ClientHandler> connectedClients; public AcceptHandler(AsynchronousServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel, List<ClientHandler> connectedClients) { this.serverSocketChannel = serverSocketChannel; this.connectedClients = connectedClients; } /** * IO 正常完成后要做的回调: 接收客户端发来的信息 -> 转发给其他客户端 */ @Override public void completed(AsynchronousSocketChannel clientChannel, Object attachment) { // 如果服务端还在线的话,要继续监听客户端的连接请求 if (serverSocketChannel.isOpen()) { serverSocketChannel.accept(null, this); } if (clientChannel != null && clientChannel.isOpen()) { ClientHandler clientHandler = new ClientHandler(clientChannel, this.connectedClients); // 添加新客户端 clientHandler.addClient(clientHandler); // 接收客户端发来的信息 ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(BUFFER); // 参数1:把客户端发来的信息读要 buffer 缓冲区中 // 参数2:将 buffer 作为附加对象传给回调对象 // 参数3:回调对象,每个客户端对应一个自己的 ClientHandler clientChannel.read(buffer, buffer, clientHandler); } } /** * IO 异常结束后要做的回调 */ @Override public void failed(Throwable exc, Object attachment) { System.out.println("AcceptHandler 发生异常了,exception: " + exc + ",attachment: " + attachment); } }ClientHandler
/** * 收到客户端发来的信息后,IO 完成后要做的回调 * * @param '<V>' The result type of the I/O operation 这里是从客户端读到了多少数据,所以是 Integer * @param '<A>' The type of the object attached to the I/O operation 附加对象的类型,这里是 ByteBuffer */ public class ClientHandler implements CompletionHandler<Integer, ByteBuffer> { private static final String QUIT = "quit"; private Charset charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8"); private AsynchronousSocketChannel clientChannel; private List<ClientHandler> connectedClients; public ClientHandler(AsynchronousSocketChannel clientChannel, List<ClientHandler> connectedClients) { this.clientChannel = clientChannel; this.connectedClients = connectedClients; } /** * IO 正常完成后要做的回调: 将客户端发来的消息转发给其他客户端 */ @Override public void completed(Integer result, ByteBuffer attachment) { ByteBuffer buffer = attachment; // 如果 attachment 为空,则表示之前服务器刚刚对 buffer 完成了读操作(即已经转发了),不需要额外的操作 if (buffer == null) { } // 如果 attachment 不为空,则表示服务器刚刚对 buffer 完成了写操作(即还没转发),现在可以来读取它 else { // 客户端异常 if (result <= 0) { removeClient(this); return; } // 将 buffer 从写模式切换为读模式 buffer.flip(); // 获取客户端发来的消息 String fwdMsg = receive(buffer); System.out.println(getClientName(this.clientChannel) + ":" + fwdMsg); // 转发 forwardMessage(clientChannel, fwdMsg); buffer.clear(); // 判断用户是否要退出 if (readyToQuit(fwdMsg)) { // 退出,移除客户端 removeClient(this); } else { // 不退出,继续监听客户端信息 clientChannel.read(buffer, buffer, this); } } } /** * IO 异常结束后要做的回调 */ @Override public void failed(Throwable exc, ByteBuffer attachment) { System.out.println("ClientHandler 发生异常了,exception: " + exc + ",attachment: " + attachment); } /** * 获取客户端发来的消息 */ private String receive(ByteBuffer buffer) { return String.valueOf(charset.decode(buffer)); } /** * 构建客户端名称 */ private String getClientName(AsynchronousSocketChannel socketChannel) { String port = "UNKNOWN_CLIENT"; try { InetSocketAddress remoteAddress = (InetSocketAddress)clientChannel.getRemoteAddress(); port = "" + remoteAddress.getPort(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return "客户端 [" + port + "] "; } /** * 判断客户端是否要下线 */ private boolean readyToQuit(String msg){ return msg.equals(QUIT); } /** * 释放资源 */ private void closeResource(Closeable closeable){ if (closeable != null){ try { closeable.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } /** * 添加新客户端 */ public synchronized void addClient(ClientHandler clientHandler) { this.connectedClients.add(clientHandler); System.out.println(getClientName(clientHandler.clientChannel) + "上线"); } /** * 移除异常客户端 */ public synchronized void removeClient(ClientHandler clientHandler) { this.connectedClients.remove(clientHandler); System.out.println(getClientName(clientHandler.clientChannel) + "下线"); closeResource(clientHandler.clientChannel); } /** * 转发 self 的消息给 connectedClients 中其他的信息 */ private synchronized void forwardMessage(AsynchronousSocketChannel self, String fwdMsg) { for (ClientHandler clientHandler: this.connectedClients) { // 不转发给自身 if (clientHandler.clientChannel.equals(self)) { continue; } // 转发给其他客户端 try { clientHandler.clientChannel.write(charset.encode(getClientName(self) + fwdMsg), null, clientHandler); }catch (Exception e){ // 捕获异常是为了避免某个客户端出意外而导致整个系统瘫痪 e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
# 6.3 客户端实现
ChatClient
public class ChatClient { private static final String LOCALHOST = "localhost"; private static final int DEFAULT_PORT = 8888; private static final String QUIT = "quit"; private static final int BUFFER = 1024; private Charset charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8"); private String host; private int port; private AsynchronousSocketChannel clientSocketChannel; public ChatClient(){ this(LOCALHOST, DEFAULT_PORT); } public ChatClient(String host, int port) { this.host = host; this.port = port; } /** * 启动客户端 */ public void start(){ try { // 获得一个客户端异步通道 clientSocketChannel = AsynchronousSocketChannel.open(); // 连接服务端 Future<Void> connectFuture = clientSocketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(this.host, this.port)); // ====================================== // 此处可以加一些其他的操作,因为是异步非阻塞的 // ====================================== // 等待连接结束 connectFuture.get(); // 处理用户输入 new Thread(new UserInputHandler(this)).start(); // 接收其他客户端的消息 ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(BUFFER); while (true) { Future<Integer> readFuture = clientSocketChannel.read(buffer); int result = readFuture.get(); if (result <= 0){ System.out.println("服务器断开..."); break; } buffer.flip(); System.out.println(charset.decode(buffer)); buffer.clear(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ExecutionException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { closeResource(clientSocketChannel); } } /** * 向服务器发送信息 */ public void send(String msg) { if (msg.isEmpty()) { return; } Future<Integer> writeFuture = clientSocketChannel.write(charset.encode(msg)); try { writeFuture.get(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ExecutionException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 判断客户端是否要下线 */ public boolean readyToQuit(String msg){ return msg.equals(QUIT); } /** * 释放资源 */ private void closeResource(Closeable closeable){ if (closeable != null){ try { closeable.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }ChatClientStarter
public class ChatClientStarter { public static void main(String[] args) { new ChatClient("localhost", 9999).start(); } }UserInputHandler
public class UserInputHandler implements Runnable { private ChatClient chatClient; public UserInputHandler(ChatClient chatClient) { this.chatClient = chatClient; } @Override public void run() { try { BufferedReader consoleReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); while (true) { String input = consoleReader.readLine(); // 向服务器发送信息 chatClient.send(input); // 检查用户是否退出 if (chatClient.readyToQuit(input)) { break; } } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
# 6.4 演示

# 五、使用场景
- BIO 方式适用于连接数目比较小且固定的架构,这种方式对服务器资源要求比较高,并发局限于应用中,JDK1.4 以前的唯一选择,但程序直观简单易理解。
- NIO 方式适用于连接数目多且连接比较短(轻操作)的架构,比如聊天服务器,并发局限于应用中,编程比较复杂,JDK1.4 开始支持。
- AIO 方式使用于连接数目多且连接比较长(重操作)的架构,比如相册服务器,充分调用 OS 参与并发操作,编程比较复杂,JDK7 开始支持。
# 六、Web 服务器
# 1. Tomcat 架构
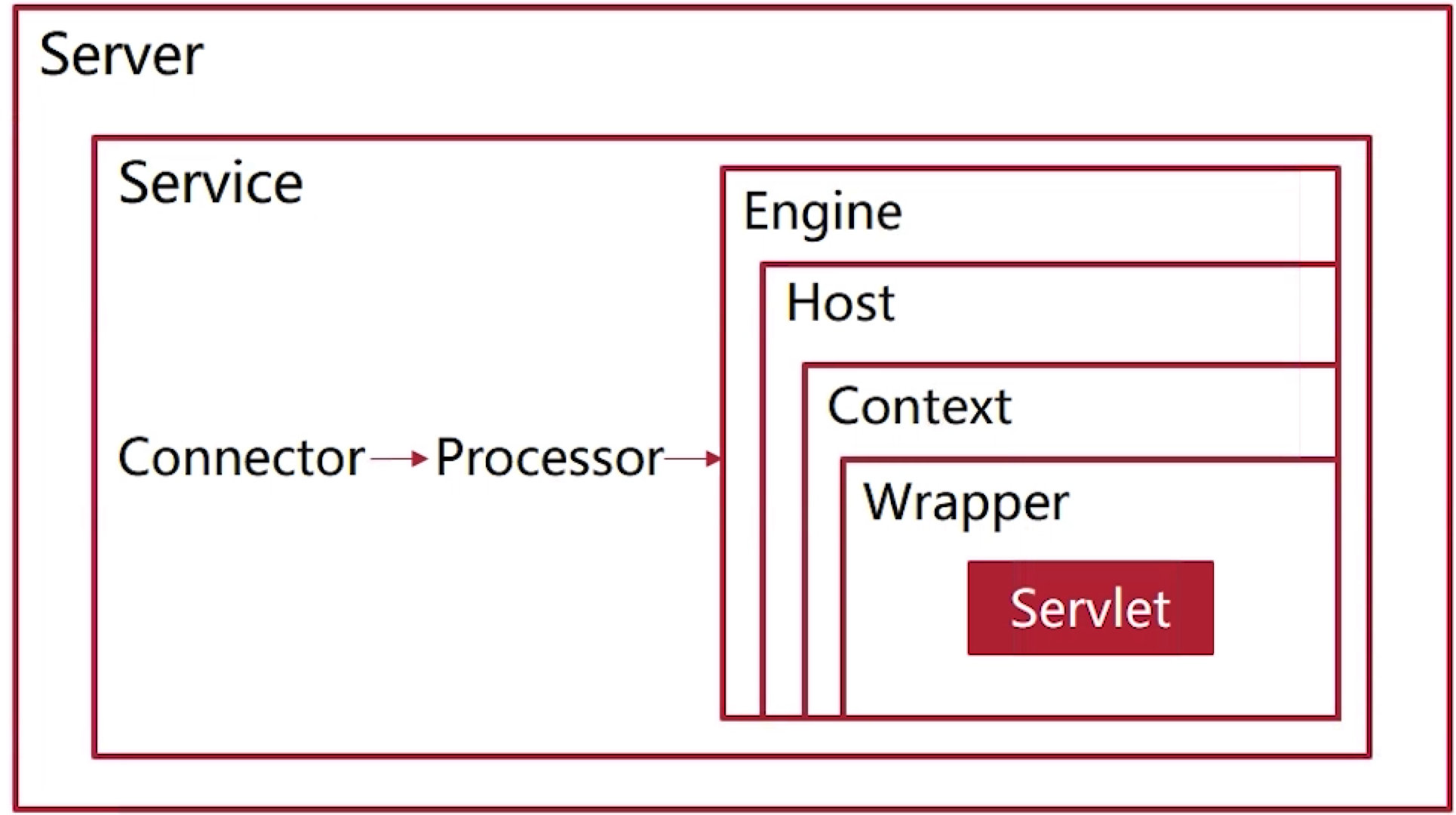
Server
- Tomcat 服务器的最顶层组件;
- 负责运行 Tomcat 服务器;
- 负责加载服务器资源和环境变量;
Service
- 集合 Connector 和 Engine 等其他重要组件的抽象组件;
- 一个 Server 可以包含多个 Server;
- 一个 Server 可以包含多个 Connector 和一个 Engine;
Connector、Processor
- Connector 提供基于不同特定协议的实现;
- Connector 负责接收请求和回传响应;
- Processor 负责接收来自 Connector 的请求并对其进行解析和处理,并派遣至 Engine 进行处理;
Engine
- Engine 可以理解为容器,Tomcat 中一个处理请求的组件;
- 容器内部的组件按照层级排列;
- Engine 是容器的顶层组件;
- Engine 根据请求的内容进行一定的解析,然后进一步派遣请求;
Host
- Host 代表一个虚拟主机;
- 一个 Engine 可以支持多个 Host 的请求;
- Engine 通过解析请求来决定将请求发送给哪一个 Host;
Context
- 每一个 Context 代表一个 Web Application;
- Tomcat 最复杂的组件之一;
- 负责应用资源管理、应用类加载、Servlet 管理和安全管理等;
Wrapper
- Wrapper 是容器的最底层组件;
- 包裹住 Servlet 实例;
- 负责管理 Servlet 实例的生命周期;
Servlet
- Servlet 是运行在 Web 服务器或应用服务器上的程序,它是作为来自 Web 浏览器或其他 HTTP 客户端的请求和 HTTP 服务器上的数据库或应用程序之间的中间层。
- 使用 Servlet,可以收集来自网页表单的用户输入,呈现来自数据库或者其他源的记录,还可以动态创建网页。
# 2. 实现简易版 Web 服务器
- 待补充。
