# 二叉树
# 简单递归
# Leetcode 104 Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/
经典递归
func maxDepth(root *TreeNode) int {
// 递归出口
if(root == nil) {
return 0
}
// 递归体
leftDepth := maxDepth(root.Left)
rightDepth := maxDepth(root.Right)
// 取高的
if leftDepth < rightDepth {
return rightDepth + 1
}
return leftDepth + 1
}
# Leetcode 111 Minimum Depth Of Binary Tree
https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-depth-of-binary-tree/
空节点不参与讨论。
func minDepth(root *TreeNode) int {
// 递归出口1
if root == nil {
return 0
}
// 递归出口2
if root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil {
return 1
}
// 只有一个子节点,不考虑空的那个子节点
if root.Left == nil {
return minDepth(root.Right) + 1
}
if root.Right == nil {
return minDepth(root.Left) + 1
}
// 左右子节点都有,就找小的
leftDepth := minDepth(root.Left)
rightDepth := minDepth(root.Right)
// 取小的
if leftDepth < rightDepth {
return leftDepth + 1
}
return rightDepth + 1
}
# Leetcode 226 Invert Binary Tree
https://leetcode.cn/problems/invert-binary-tree/
func invertTree(root *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
// 递归出口1
if root == nil {
return root
}
// 递归体
left := invertTree(root.Left)
right := invertTree(root.Right)
// 左右交换
root.Left = right
root.Right = left
return root
}
# Leetcode 100 Same Tree
https://leetcode.cn/problems/same-tree/
func isSameTree(p *TreeNode, q *TreeNode) bool {
// 递归出口1
if p == nil && q == nil {
return true
}
// 递归出口2
if p == nil || q == nil {
return false
}
// 递归出口3
if p.Val != q.Val {
return false
}
// 递归体:当前节点相同了,再比较左右子树
return isSameTree(p.Left, q.Left) && isSameTree(p.Right, q.Right)
}
# Leetcode 101 Symmetric Tree
https://leetcode.cn/problems/symmetric-tree/
思路一:
- 先反转右子树,再比较左右子树是否相等;
思路二:
- 层次遍历,空填 null,判断每一次是否是回文;
思路三:
- 后序遍历,空填 null,判断结果是否是回文;
思路四:
- 递归:左左 == 右右,左右 == 右左
下面展示思路四的代码:
func isSymmetric(root *TreeNode) bool {
if root == nil {
return true
}
return symmetric(root.Left, root.Right)
}
func symmetric(node1 *TreeNode, node2 *TreeNode) bool {
// 递归出口1
if node1 == nil && node2 == nil {
return true
}
// 递归出口2
if node1 == nil || node2 == nil {
return false
}
// 递归出口3
if node1.Val != node2.Val {
return false
}
// 递归体:当前值相同再比较是否相同
// 左左 = 右右
// 左右 = 右左
return symmetric(node1.Left, node2.Right) && symmetric(node1.Right, node2.Left)
}
# Leetcode 222 Count Complete Tree Nodes
https://leetcode.cn/problems/count-complete-tree-nodes/
func countNodes(root *TreeNode) int {
// 递归出口1
if root == nil {
return 0
}
// 递归出口2:左右全空
if root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil {
return 1
}
// 递归出口3:空一个的话,完全二叉树只可能空右
if root.Right == nil {
return 2
}
return 1 + countNodes(root.Left) + countNodes(root.Right)
}
# Leetcode 110 Balanced Binary Tree
https://leetcode.cn/problems/balanced-binary-tree/
func isBalanced(root *TreeNode) bool {
// 递归出口1:空树,天然二叉平衡
if root == nil {
return true
}
// 递归出口2:左右子树高度相差超过 1
if math.Abs(float64(depth(root.Left)) - float64(depth(root.Right))) > 1 {
return false
}
// 递归体:递归检查左右子树是否是平衡二叉树
return isBalanced(root.Left) && isBalanced(root.Right)
}
// 计算高度
func depth(node *TreeNode) int {
if node == nil {
return 0
}
left := depth(node.Left)
right := depth(node.Right)
if left < right {
return right + 1
}
return left + 1
}
# 后序遍历
# Leetcode 236 Lowest Common Ancestor Of A Binary Tree
https://leetcode.cn/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree/
遇到这个题目首先想的是要是能 自底向上 查找就好了,这样就可以找到公共祖先了。
- 自底向上 -> 回溯
- 后序遍历 -> 回溯
后序遍历就是天然的回溯过程,最先处理的一定是叶子节点。
下来就看如何判断一个节点是节点 q 和节点 p 的公共祖先呢:
- 如果找到一个节点,发现左子树出现结点 p,右子树出现节点 q,或者左子树出现结点 q,右子树出现节点 p,那么该节点就是节点 p 和 q 的最近公共祖先。
- 使用后序遍历,回溯的过程,就是从低向上遍历节点,一旦发现如何这个条件的节点,就是最近公共节点了。
首先确定递归终止条件:
- 空节点,直接返回;
- 找到了 p 或者 q,那么 p 或者 q 便是祖先,返回;
在确定递归体之前,先思考返回值的情况,共有四种:p,q,nil,最近公共祖先。
故递归体为:
- 递归左右子树,拿到返回值 l 和 r;
- 如果 l 和 r 都不为空,表示左右子树都有返回值,那不可能找到两个最近公共祖先,所以 l 和 r 就是 p 和 q 本身,那么 root 就是最近公共祖先;
- 如果 l 和 r 中只有一个不为空,那么 l 或 r 就是公共祖先
func lowestCommonAncestor(root, p, q *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
// 递归出口1:空树
if root == nil {
return nil
}
// 递归出口2:p 和 q 中有一个就是 root
if p == root || q == root {
return root
}
// 祖先只可能在三个地方:左子树,root,右子树
// 递归在左右子树找
// 四种返回值:公共祖先,p,q,nil
l := lowestCommonAncestor(root.Left, p, q)
r := lowestCommonAncestor(root.Right, p, q)
// ① 如果 l 和 r 都不为 nil,那么就是 p 和 q 本身,不可能是公共祖先
if l != nil && r != nil {
return root
} else if l != nil { // ② l 和 r 中只有一个不为空,那就是找到公共祖先了,直接返回
return l
} else if r != nil {
return r
}
// ③ 没找到(其实不可能)
return nil
}
# 递归路径
# Leetcode 112 Path Sum
https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-sum/
本题要注意一下递归出口:该路径,必须是从根到叶子节点,而不能是中间节点
func hasPathSum(root *TreeNode, targetSum int) bool {
// 递归出口1:空树必 false
if root == nil {
return false
}
// 递归出口2:root 是叶子节点,且 val == targetSum
if root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil {
return root.Val == targetSum
}
return hasPathSum(root.Left, targetSum - root.Val) || hasPathSum(root.Right, targetSum - root.Val)
}
# Leetcode 404 Sum Of Left Leaves
https://leetcode.cn/problems/sum-of-left-leaves/
本题的关键是只要左叶子节点的,所以可以加一个标志 left 来判断当前 node 是否是左节点,当该节点是叶子节点的时候,如果它是左节点,那就累加它的 Val,最终将所有左叶子节点的 Val 都累加起来,返回即为答案。
func sumOfLeftLeaves(root *TreeNode) int {
// 题目保证 root 不为空
return help(root.Left, true) + help(root.Right, false)
}
// left 用来表示当前节点是否是左节点
func help(node *TreeNode, left bool) int {
// 递归出口1:空那就是0
if node == nil {
return 0
}
// 递归出口2:是叶子节点
if node.Left == nil && node.Right == nil{
// 判断是否是左叶子节点
if left {
return node.Val
}
}
return help(node.Left, true) + help(node.Right, false)
}
# Leetcode 267 Binary Tree Paths
https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-paths/
本题的关键在于要保存路径,确定好递归出口。另外,还需要关注各个语言的指针操作,避免一个指针操作了多个 path 上的值。
func binaryTreePaths(root *TreeNode) []string {
var path []int
return transfer(help(root, path))
}
func help(root *TreeNode, path []int) [][]int {
// 递归出口1:空树
if root == nil {
return nil
}
var res [][]int
path = append(path, root.Val)
// 递归出口2:到叶子节点了
if root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil {
return append(res, path)
}
// 递归左子树
if root.Left != nil {
p1 := make([]int, len(path))
copy(p1, path)
res = append(res, help(root.Left, p1)...)
}
// 递归右子树
if root.Right != nil {
p2 := make([]int, len(path))
copy(p2, path)
res = append(res, help(root.Right, p2)...)
}
return res
}
// 输出路径
func transfer(tmp [][]int) []string {
var res []string
for i:=0; i<len(tmp); i++ {
t := tmp[i]
s := ""
for j:=0; j<len(t); j++ {
s += strconv.Itoa(t[j])
if j != len(t) - 1 {
s += "->"
}
}
res = append(res, s)
}
return res
}
# Leetcode 113 Path Sum ii
https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-sum-ii/
本题思路跟 267 非常像,只是递归出口的条件变了,需要根据 targetSum 来确定路径是否满足条件。
func pathSum(root *TreeNode, targetSum int) [][]int {
var path []int
return help(root, targetSum, path)
}
func help(root *TreeNode, targetSum int, path []int) [][]int {
var res [][]int
// 递归出口1:空树
if root == nil {
return nil
}
path = append(path, root.Val)
// 递归出口2:到叶子节点
if root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil {
// 该路径不满足条件
if targetSum != root.Val {
return nil
}
// 该路径满足条件
return append(res, path)
}
// 递归左子树
if root.Left != nil {
p1 := make([]int, len(path))
copy(p1, path)
res = append(res, help(root.Left, targetSum - root.Val, p1)...)
}
// 递归右子树
if root.Right != nil {
p2 := make([]int, len(path))
copy(p2, path)
res = append(res, help(root.Right, targetSum - root.Val, p2)...)
}
return res
}
# Leetcode 129 Sum Root To Leaf Numbers
https://leetcode.cn/problems/sum-root-to-leaf-numbers/submissions/
本题跟 267 基本一致,只是“输出方式”不同罢了。 267 要的是把路径拼成 “1->2->3” 之类的,而本题,需要把路径分别合并成一个数字,然后再求和。
func sumNumbers(root *TreeNode) int {
var path []int
return transfer(help(root, path))
}
func help(root *TreeNode, path []int) [][]int {
// 递归出口1:空树
if root == nil {
return nil
}
var res [][]int
path = append(path, root.Val)
// 递归出口2:到叶子节点了
if root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil {
return append(res, path)
}
// 递归左子树
if root.Left != nil {
p1 := make([]int, len(path))
copy(p1, path)
res = append(res, help(root.Left, p1)...)
}
// 递归右子树
if root.Right != nil {
p2 := make([]int, len(path))
copy(p2, path)
res = append(res, help(root.Right, p2)...)
}
return res
}
// 将每条路径合并成一个数字,并求和
func transfer(tmp [][]int) int {
var res []string
// 合并成数字
for i:=0; i<len(tmp); i++ {
t := tmp[i]
s := ""
for j:=0; j<len(t); j++ {
s += strconv.Itoa(t[j])
}
res = append(res, s)
}
num := 0
// 求和
for _, n := range res {
i, _ := strconv.Atoi(n)
num += i
}
return num
}
# 双重递归
# Leetcode 437 Path Sum III
https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-sum-iii/
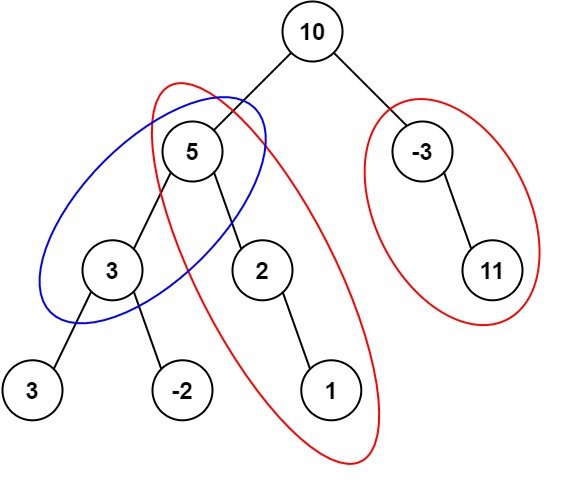
本题要求的路径,不需要从根节点出发,也不需要在叶子节点结束,所以:
- 我们需要尝试以每一个节点为起始点来寻找合适的路径;
- 找到路径后,不要退出,而是继续走完当前路径,看看还有没有符合条件的;
这就用到了双重递归:
- 定义一个 rootSum 方法,表示从 root 为起始点的来寻找满足条件的路径个数;
- 在 pathSum 中,先以 root 为起始点找,再分别以 root.Left 和 root.Right 为起始点寻找;
- 最后合并,即为答案。
func pathSum(root *TreeNode, targetSum int) int {
// 递归出口1:空树
if root == nil {
return 0
}
// 以 root 为起点寻找
res := rootSum(root, targetSum)
// 再递归左右子树
res += pathSum(root.Left, targetSum)
res += pathSum(root.Right, targetSum)
return res
}
// 从 root 出发寻找的路径
func rootSum(root *TreeNode, targetSum int) int {
// 递归出口1:空树
if root == nil {
return 0
}
res := 0
// 找到路径,但是不退出,继续往下找
if root.Val == targetSum {
res ++
}
// 递归出口2:叶子节点
if root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil {
return res
}
// 递归左子树
if root.Left != nil {
res += rootSum(root.Left, targetSum - root.Val)
}
// 递归右子树
if root.Right != nil {
res += rootSum(root.Right, targetSum - root.Val)
}
return res;
}
# 二分搜索树
# Leetcode 235 Lowest Common Ancestor Of A Binary Search Tree
https://leetcode.cn/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-search-tree/
因为本题的树是二分搜索树,是天然有序的。于是可以分为 4 种情况:
- p 和 q 都在 root 的左边,那最近公共祖先只可能在 root.Left 寻找;
- p 和 q 都在 root 的右边,那最近公共祖先只可能在 root.Right 寻找;
- p 和 q 在 root 的两边,那最近公共祖先就是 root;
- p 和 q 其中之一就是 root,那最近公共祖先就是 root;
func lowestCommonAncestor(root, p, q *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
// 情况1:p,q 分居 root 两侧,那最近公共祖先就是 root
if p.Val <= root.Val && q.Val >= root.Val {
return root
}
if p.Val >= root.Val && q.Val <= root.Val {
return root
}
// 情况2:p 或 q 本身就是 root
if p == root || q == root {
return root
}
// 情况3:p,q 都在 root 左侧,那只能在 root.Left 寻找
if p.Val < root.Val && q.Val < root.Val {
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.Left, p,q )
}
// 情况4:p,q 都在 root 右侧,那只能在 root.Right 寻找
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.Right, p, q)
}
# Leetcode 98 Validate Binary Search Tree
https://leetcode.cn/problems/validate-binary-search-tree/
根据二分搜索树的定义,
func isValidBST(root *TreeNode) bool {
return help(root, math.MinInt64, math.MaxInt64)
}
func help(root *TreeNode, lower, upper int64) bool {
// 递归出口1:空树也是二分搜索树
if root == nil {
return true
}
// 递归出口2:root 不在 lower 和 upper 之间,不符合规定
if int64(root.Val) >= upper || int64(root.Val) <= lower {
return false
}
// 递归左右子树,并确定新的区间
return help(root.Left, lower, int64(root.Val)) && help(root.Right, int64(root.Val), upper)
}
# Leetcode 450 Delete Node In a BST
https://leetcode.cn/problems/delete-node-in-a-bst/
如果被删除节点存在,那么有三种情况:
- 叶子节点:直接删除;
- 只有一个子树,将该子树移到当前节点位置;
- 有两个子树,从左子树中找到最大的节点替代当前节点,或者从右子树中找最小的节点替代当前节点,即找“左中最右”或者“右中最左”
func deleteNode(root *TreeNode, key int) *TreeNode {
if root == nil {
return nil
}
if root.Val == key {
// 情况1:叶子节点,直接删除
if root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil {
return nil
}
// 情况2:只有一个子节点,返回子节点
if root.Left == nil {
return root.Right
}
if root.Right == nil {
return root.Left
}
// 情况3:有2个子节点,可找“左中最右”或“右中最左”,这里找“右中最左”
pre := root
cur := root.Right
for cur.Left != nil {
pre = cur
cur = cur.Left
}
// 此时 cur 已经是右中最左了,将 cur 移动 root 的位置,并释放原 root
if pre == root {
cur.Left = root.Left
return cur
}
pre.Left = cur.Right
cur.Left = root.Left
cur.Right = root.Right
root = cur
return root
}
// 递归左子树
if key < root.Val {
root.Left = deleteNode(root.Left, key)
} else {
// 递归右子树
root.Right = deleteNode(root.Right, key)
}
return root
}
# Leetcode 108 Convert Sorted Array To Binary Search Tree
https://leetcode.cn/problems/convert-sorted-array-to-binary-search-tree/
数组有序,二分搜索树也有序,要二分搜索树平衡,我们就要一直取中间值作为根节点,然后再分别以此策略建立左右子树。
func sortedArrayToBST(nums []int) *TreeNode {
return help(nums, 0, len(nums) - 1)
}
// 左闭右闭
func help(nums []int, start, end int) * TreeNode {
if start > end {
return nil
}
// 情况1:只有一个值,直接建立节点返回
if start == end {
return &TreeNode{Val: nums[start]}
}
// 情况2:找中间值作为中间节点,然后再分治建立左右节点
midIndex := (start + end ) / 2
root := &TreeNode{Val: nums[midIndex]}
root.Left = help(nums, start, midIndex - 1)
root.Right = help(nums, midIndex + 1, end)
return root
}
# Leetcode 230 Kth Smallest Element In a BST
https://leetcode.cn/problems/kth-smallest-element-in-a-bst/
思路一:中序遍历
因为二分搜索树天然有序,所以中序遍历后得到的结果便是从小到大的有序数组 elems,我们取 elems[k-1] 即为答案。
优化:可以加一个计数器,我们扫到第 k 个的时候停下,即可。
var count = 0
var ans = 0
func kthSmallest(root *TreeNode, k int) int {
inorderTraversal(root, k)
return ans
}
// 中序遍历
func inorderTraversal(root *TreeNode, k int) {
if root == nil {
return
}
inorderTraversal(root.Left, k)
count ++
if count == k {
ans = root.Val
return
}
inorderTraversal(root.Right, k)
}
